Periodontics quiz
Advanced
Quiz 2
Diagnosis of periodontal diseases (Advanced)
Results
CONGRATULATIONS!
Don’t give up, try again!
#1. What are the different classes of periodontal pockets? Select the most correct answer.
#2. Periodontal pockets extending into areas of vertical bone loss are identified as:
#3. Which of the following teeth may have furcation involvement if affected by periodontitis?
#4. Class II furcation involvement refers to ______________horizontal bone/attachment loss in the area of tooth furcation.
#5. Subclass A furcation involvement refers to _____________ vertical bone/attachment loss in the area of tooth furcation.
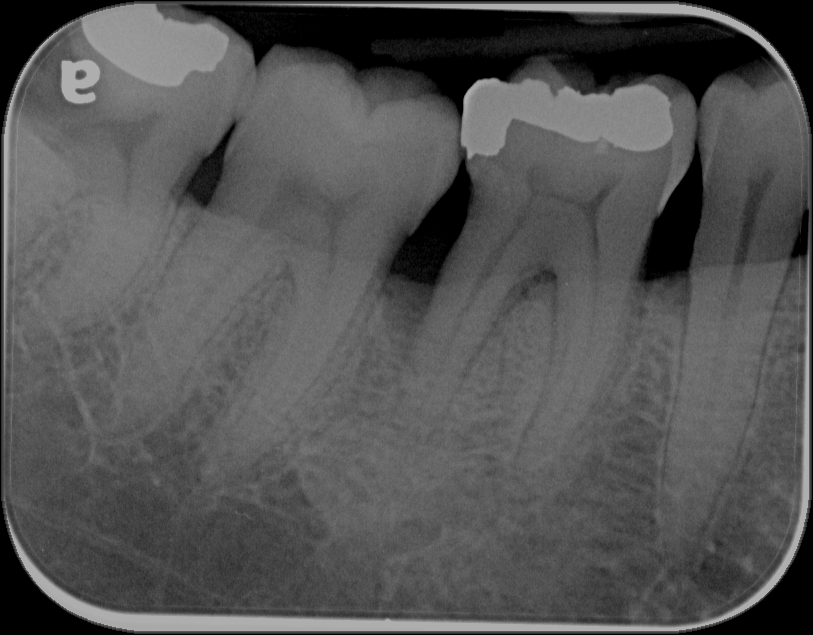
#6. Which of the molars shows furcation involvement and which subclass would you assign to the furcation involvement?